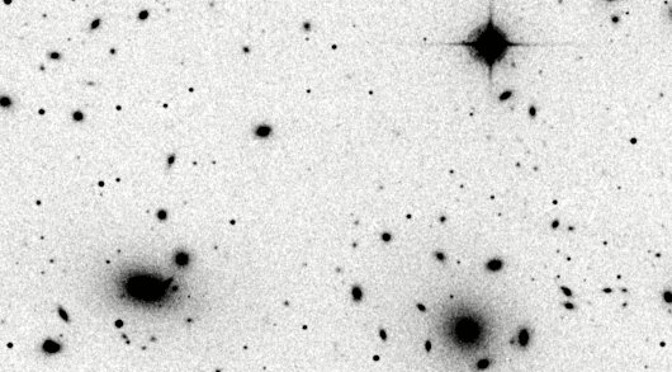
Seven to 10 billion years ago, a bunch of galaxies fell in with a bad crowd at the Coma cluster — a galactic group comprising thousands of their ilk. That crash “quenched” the ill-fated galaxies. They’d never again burn with hot, young stars. But the crash should have done more than shut down the unfortunate galaxies’ stellar birth rate. It should have strewn their stars across space.
So what kept these cosmic corpses intact? Read on, if you dare (OK, so the title is a bit of a hint …).